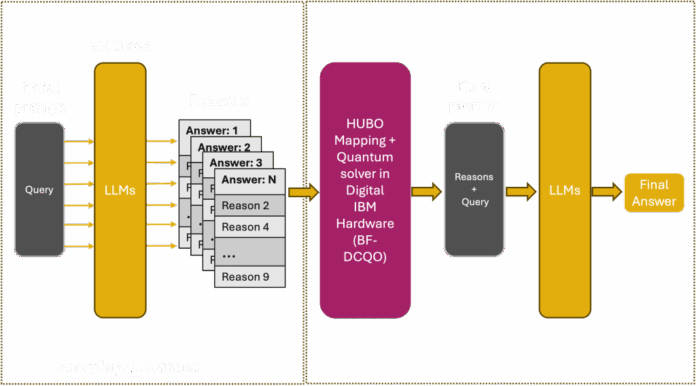
Large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 are vital across sectors such as finance and medicine, yet their reasoning capabilities can be inconsistent and opaque. Recent research aims to optimize reasoning by framing it as a combinatorial problem, utilizing quantum processors to analyze numerous candidate explanations. This method begins by generating a diverse pool of reasoning fragments, which are then optimized using a Higher-Order Unconstrained Binary Optimization (HUBO) Hamiltonian. Quantum hardware, particularly the Bias-Field Digitised Counterdiabatic Quantum Optimisation (BF-DCQO) algorithm, allows for the parallel evaluation of complex interactions in reasoning tasks, significantly enhancing accuracy. Tests showcase this technology’s superiority over classical methods, achieving better performance in reasoning benchmarks. This advancement signifies a pivotal move toward Quantum Intelligence (QI), where quantum processing augments neural networks by ensuring logical coherence and transparency in AI outputs. As quantum technology evolves, it holds promise for more reliable, real-time decision-making across regulated industries.
Source link
Share
Read more