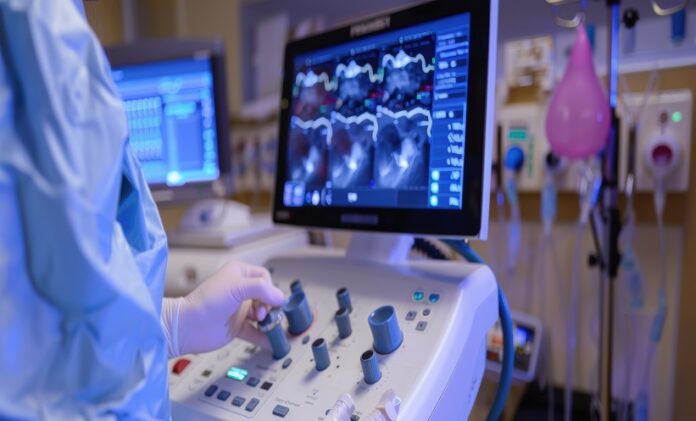
A groundbreaking study has unveiled a new artificial intelligence (AI) model capable of accurately identifying cardiac amyloidosis (CA) from other heart conditions on echocardiograms. CA, characterized by abnormal protein accumulation in heart muscle, often mimics heart failure symptoms, complicating timely diagnosis. Conducted across 18 international sites, researchers trained a deep learning algorithm using echocardiographic data from 2,612 participants, half diagnosed with CA. The model, based on a convolutional neural network, showcased impressive diagnostic accuracy with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) of 0.93, achieving sensitivity of 85% and specificity of 93%. The AI outperformed traditional diagnostic methods, making it a promising tool for early, non-invasive CA screening using standard transthoracic echocardiograms. This advancement could significantly enhance early detection, allowing for prompt intervention and better survival outcomes for patients with cardiac amyloidosis.
Reference: Slivnick JA et al. European Heart Journal, 2025.
Source link