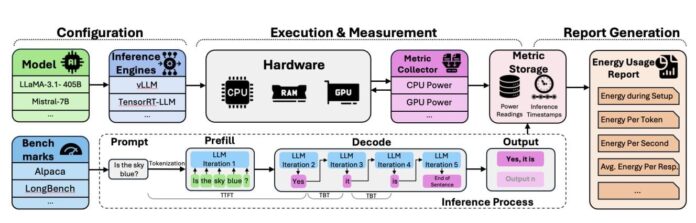
The increasing use of large language models (LLMs) has led to a rise in energy consumption during inference, a critical aspect for developers and researchers focusing on sustainable AI. Addressing this challenge, researchers from Texas Tech University and Texas Advanced Computing Center introduced TokenPowerBench, an innovative benchmark for measuring LLM power usage. This tool features an easy-to-use configuration system, a power measurement layer utilizing vendor telemetry APIs, and a comprehensive metrics pipeline that captures detailed energy consumption across various inference stages.
By enabling precise tracking of GPU, CPU, and memory power, TokenPowerBench aids in optimizing settings for enhanced energy efficiency. The research highlights how software optimizations, such as quantization and specialized frameworks like Nvidia’s TensorRT-LLM, can significantly reduce energy costs. Furthermore, findings indicate that while larger models consume more energy per token, optimizing batch sizes and parallelism can yield substantial savings. Overall, TokenPowerBench paves the way for a more sustainable AI future.
Source link