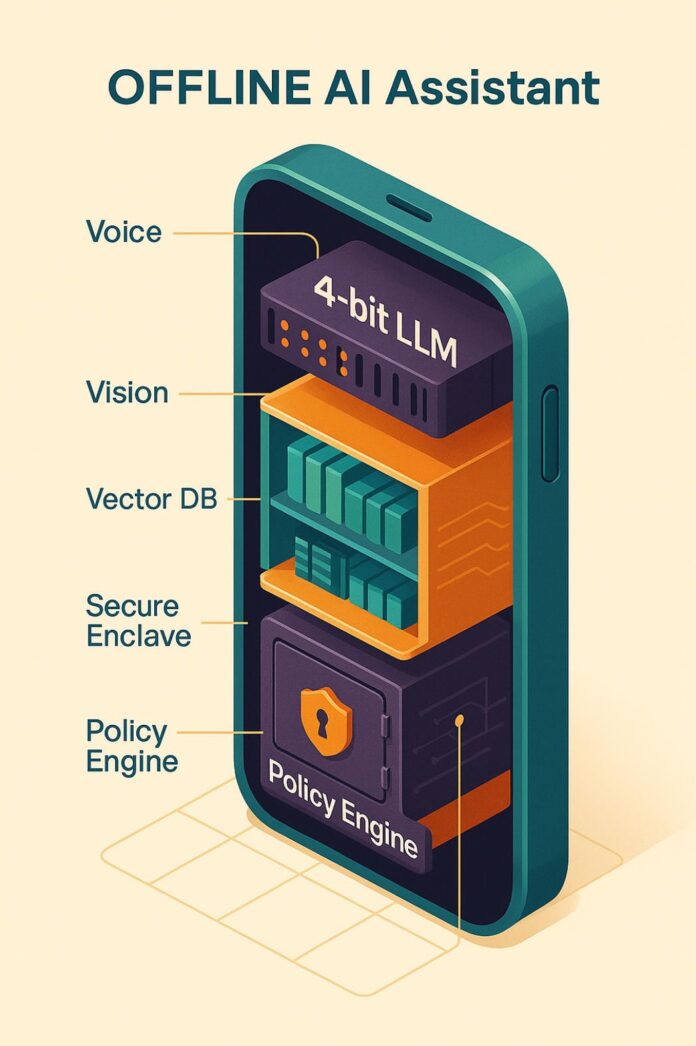
OpenAI’s introduction of a compact offline AI model marks a significant evolution in artificial intelligence, particularly for African markets grappling with high data costs and unreliable connectivity. This innovative model allows AI features—like voice transcription, translation, and image analysis—to operate fully on-device, eliminating the need for cloud access. For regions like South Africa, where data expenses are substantial, developers can now create AI applications that enhance user experience without incurring extra data costs. This shift could transform Africa’s mobile ecosystem, enabling app creators to deliver cost-efficient solutions in sectors like telehealth, digital banking, and education. Additionally, the introduction of offline AI raises security and regulatory questions, necessitating new frameworks for oversight. As developers in Nigeria, Kenya, and South Africa adapt to this technology, those unable to transition may risk obsolescence by 2026. OpenAI’s offline model promises to revolutionize digital inclusion and mobile innovation across the continent.
Source link
Share
Read more