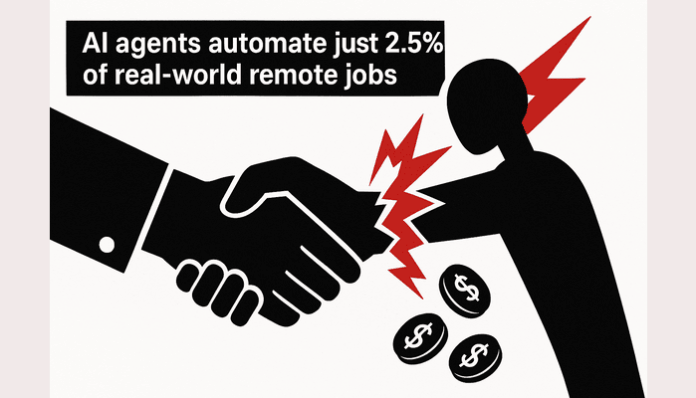
A recent study, the ‘RemoteLabourr Index (RLI): Measuring AI Automation of Remote Work,’ shows that advanced AI agents complete less than 3% of real-world freelance projects. Developed by the Centre for AI Safety and Scale AI, the RLI evaluates 240 freelance projects across diverse industries, demonstrating that current AI systems, including Manus and others like GPT-5 and Claude Sonnet 4.5, are far from capable of automating valuable remote work. Despite technological advancements, these systems achieved automation rates below 3%, indicating a significant gap between lab benchmarks and real market demands. The study highlights the necessity of assessing AI capabilities through practical economic metrics, rather than theoretical benchmarks, which reveals low displacement risk for freelance workers. Common AI shortcomings include incomplete outputs and poor quality, underscoring the ongoing need for human expertise in remote labor. Incremental improvements are noted, yet AI performance still significantly lags behind human capabilities.
Source link
Share
Read more