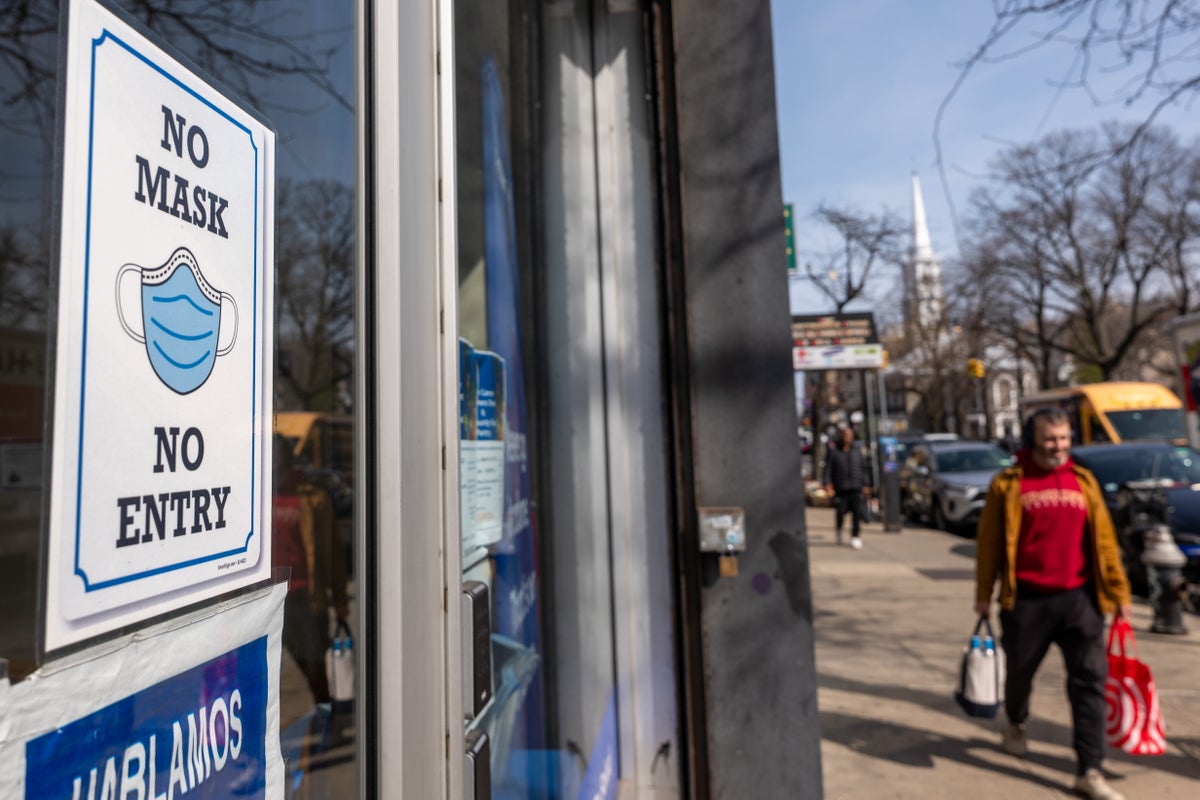
Builder.ai, a London-based startup once valued at $1.5 billion and backed by Microsoft and Qatar’s sovereign wealth fund, has filed for bankruptcy. The company marketed its app development platform as “AI-powered,” but investigations revealed that around 700 Indian engineers were manually coding applications, rather than using artificial intelligence. Despite its claims, Builder.ai failed to deliver on promised revenues, inflating its 2024 projections by 300%, which led to lender Viola Credit seizing $37 million in May 2025. Founder Sachin Dev Duggal promised $220 million in sales, but an audit revealed only $50 million. Previous reports since 2019 highlighted the reliance on human labor, prompting a lawsuit from a former employee alleging deception. The company’s collapse underscores issues of “AI washing,” where traditional services are misrepresented as cutting-edge technology to attract investments. Following the bankruptcy, 1,000 employees lost their jobs, and the company owes substantial debts to major cloud service providers.
Source link
Unveiling the Tactics of a Billion-Dollar London Startup: How Microsoft’s Backed Venture Used 700 Indian Engineers to Simulate AI
OpenAI Reveals That Many Recent ChatGPT Misuses Appear to Originat from China – WSJ
OpenAI reported that a substantial portion of recent ChatGPT misuses can be traced back to China. The company noted that many of these incidents involved attempts to manipulate the AI for malicious purposes, such as spreading misinformation or conducting scams. OpenAI emphasized its commitment to addressing these challenges and enhancing the model’s safety features to prevent misuse. They revealed ongoing collaboration with authorities and tech platforms to identify and mitigate harmful activities tied to the AI’s capabilities. OpenAI also mentioned the importance of responsible usage, urging users worldwide to follow guidelines to maintain ethical standards. By focusing on improving security measures, the organization aims to foster a safer environment for AI interactions and to curtail the exploitation of its technologies. This revelation underscores the global concerns regarding AI’s potential misuse and the need for effective regulations and oversight.
Source link
Access Denied
Access to the requested content has been blocked due to a security issue. An Incident ID is provided for reference: 20250606T172557Z-15c9cc5c4b6pwwlkhC1HYDa33c0000000skg000000002yed. If you think this blockage is a mistake, you are advised to contact support and include the Incident ID for further assistance.
Source link
Quick Dive: A Rapid Review of a Study with SciSummary
SciSummary is an AI tool designed to help academics quickly interpret complex research papers and scientific articles. It efficiently generates structured summaries, podcasts, and slideshows, emphasizing clarity without compromising critical insights. The straightforward interface allows users to upload documents directly or via email, catering to a wide range of academic fields. Key features include customizable summaries, analysis of figures and tables, reference management, and multi-document chat. While it excels in summarizing, SciSummary may oversimplify intricate concepts and lacks a dedicated mobile app. Its pricing structure includes free trials and discounted plans for students, making it accessible for researchers and academics. The review compares SciSummary to alternatives like Scholarcy, Explainpaper, and Summarizer.org; each serves different user needs, from collaborative features to clear explanations. Overall, SciSummary is a valuable tool for anyone in the scientific community seeking to streamline their research process.
Source link
Preventing the Next Pandemic: The Role of AI in Early Detection and Response
Researchers at Johns Hopkins and Duke universities have developed an innovative AI tool, PandemicLLM, aimed at predicting the spread of infectious diseases and potentially preventing future pandemics. Unlike traditional models that relied on historical data, PandemicLLM utilizes real-time information such as infection rates, new variants, and government policies, enabling more accurate predictions of disease patterns and hospitalization trends one to three weeks ahead. The tool demonstrated its efficacy by retroactively analyzing data from the Covid pandemic, outperforming existing forecasting methods. With ongoing health threats like H5N1 bird flu and vaccine hesitancy, the researchers stress the necessity of advanced modeling for effective public health responses. As pandemics are inevitable, PandemicLLM aims to inform policies that could mitigate the impact of future outbreaks, addressing the complexities unveiled during Covid-19 and supporting public health infrastructures in their preparedness and response efforts.
Source link
Trump and Musk Join Forces: The Showdown Between OpenAI and Anthropic in Coding
OpenAI’s acquisition of Windsurf has prompted Anthropic to halt support for the coding app, indicating a competitive tension in the AI landscape. Mary Meeker’s report forecasts unprecedented AI growth, aligning with a surge in IPOs and M&A activities, notably with Circle’s stablecoin. However, developers face existential risks as major LLM companies, like OpenAI and Anthropic, navigate their influence over platform-dependent apps. This scenario mirrors past distresses experienced by developers on dominant platforms like Windows and Facebook. Anthropic’s recent restrictions on Windsurf highlight the vulnerability of AI tools dependent on external platforms. Meanwhile, as LLM providers, including OpenAI and Anthropic, vie for market share, they must balance their development relationships while other players, like Cursor, flourish independently. As the AI sector matures, finding equilibrium between competition and cooperation will be critical for both major LLMs and emerging developers.
Source link
OpenAI Executive Explores Potential Stargate Data Center Locations Across APAC – Report – Data Center Dynamics
An OpenAI executive is touring the Asia-Pacific region to explore potential sites for a new Stargate data center. The initiative aims to enhance the company’s infrastructure to support its AI advancements and meet the growing demand for computational power. Locations being considered include key technology hubs known for their robust data center markets. This move aligns with OpenAI’s strategy to expand its global footprint and improve service delivery in various regions, particularly in fast-evolving markets across Asia. The choice of sites will likely reflect factors such as connectivity, energy availability, and regulatory environment, ensuring efficient and sustainable operations. The results of this tour could significantly impact OpenAI’s operational capabilities, enabling faster processing and development of AI models. As demand for AI technologies continues to rise, establishing new data centers is essential for maintaining competitive advantage and continuing innovation in the AI sector.
Source link
OpenAI Retains Deleted ChatGPT Conversations in Response to NYT Lawsuit
OpenAI is compelled to retain deleted ChatGPT conversations “indefinitely” due to a court order related to a copyright lawsuit filed by The New York Times. OpenAI’s COO, Brad Lightcap, criticized the ruling as an infringement on privacy norms and stated the company is appealing this decision. The court mandated that OpenAI preserve all output log data, overriding its usual policy where deleted chats are retained for only 30 days. This order impacts various ChatGPT user tiers, except for ChatGPT Enterprise and Edu customers with zero data retention agreements. OpenAI assured that the data will remain confidential, accessible only to a limited legal and security team. The New York Times alleges that OpenAI and Microsoft unlawfully used its articles to train their AI, arguing that retaining user data is necessary for their legal case. OpenAI CEO Sam Altman emphasized their commitment to user privacy and vowed to challenge demands that compromise it.
Source link
Transforming Industries: How AI Tools Optimize Processes and Shift Perspectives
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the filmmaking process, moving beyond its previous role as a background tool to enhance creativity. Notably, in films like The Brutalist, AI has been utilized to modify foreign accents without altering the original actors’ voices, while in Emilia Pérez, it blended the lead actress’s vocals with another singer’s to expand her range. This shift in Hollywood’s perception of AI marks a departure from earlier fears, particularly during past strikes by writers and actors. In animation, production timelines are rapidly reducing; for instance, it may soon be possible to create an anime film in under three hours, compared to the three years it took for The Lion King. Concurrently, the federal government is rebranding the AI Safety Institute to the Center for AI Standards and Innovation, emphasizing collaboration with tech companies to promote innovation while managing AI risks. Overall, these changes suggest a more integrated future for AI in various sectors.