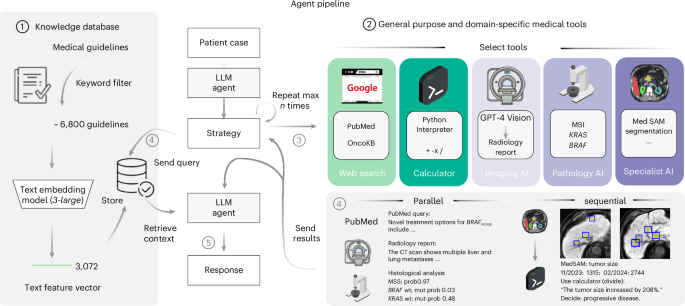
This study utilized fully anonymized, publicly accessible patient data, complying with ethical standards outlined by the Declaration of Helsinki and receiving approval from the Technical University Dresden’s Ethics Commission. The research aimed to compile a high-quality dataset focusing on medical and oncology guidelines from six selected sources, including MDCalc and Clinical Practice Guidelines. A significant challenge arose in extracting text from PDFs due to their inconsistent structures. To mitigate this, the GROBID tool was employed to standardize data and maintain its integrity. The research utilized a Robustly Augmented Generation (RAG) architecture, combining retrieval with generative capabilities of large language models (LLMs) for medical queries. An array of tools enabled the LLM to conduct searches, analyze imaging data, and access genetic databases for precision oncology. Evaluation methods for model performance involved structured assessments by clinicians regarding output accuracy, tool usage, and adherence to medical guidelines, ensuring comprehensive evaluation of the LLM’s capabilities in clinical scenarios.
Source link
Share
Read more