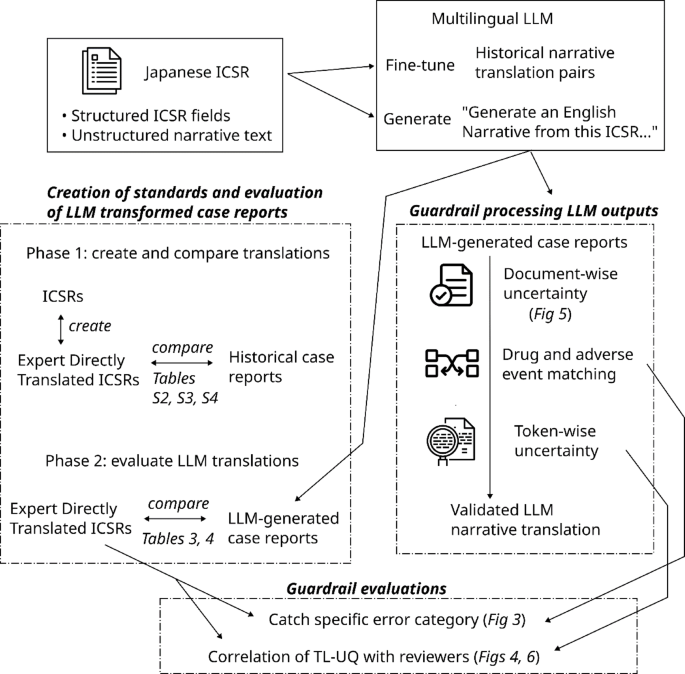
The study outlines a comprehensive workflow for processing Individual Case Safety Reports (ICSRs) using advanced language models (LLMs). Sourced from GSK’s global safety database, the dataset includes over 4 million ICSRs, emphasizing original submissions pre-review. Key components include the creation of a multilingual corpus, with data in Japanese, Spanish, French, and German, for fine-tuning LLMs. The study evaluates three models, assessing translation quality through expert reviews and automated guardrails designed to ensure accuracy. These guardrails include Document-Level Uncertainty Quantification (DL-UQ) to filter non-ICSR documents, and a MISMATCH check to identify discrepancies in drug names. Hyperparameter tuning during the generation phase optimized output quality, validated through measures like BLEU scores. The evaluation involved human expertise to ensure reliability and clinical acceptability. Overall, the robust methodology enhances ICSR processing and translation, crucial for pharmacovigilance and regulatory compliance in global pharmaceutical safety reporting.
Source link
Establishing Safeguards for Large Language Models in Pharmacovigilance and Critical Medical Safety Environments
Share
Read more