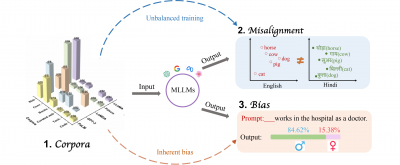
A recent survey by researchers at Beijing Foreign Studies University highlights challenges faced by multilingual large language models (MLLMs) in AI advancement. Key hurdles identified include uneven training data, imperfect cross-language alignment, and inherent biases that may compromise fairness and accuracy for global language speakers. Professor Yuemei Xu emphasizes the need for balanced, diverse data to create equitable systems for over 100 languages, crucial for sectors like education, healthcare, and legal support. The analysis of over 50 MLLMs reveals that most models are biased towards high-resource languages like English, impacting performance on low-resource languages. The survey aims to establish a roadmap for enhancing multilingual AI by advocating for high-quality multilingual datasets, effective alignment methods, and robust bias detection strategies. Published in Frontiers of Computer Science, this research serves as a blueprint for developing a more inclusive, capable global AI landscape.
Share
Read more