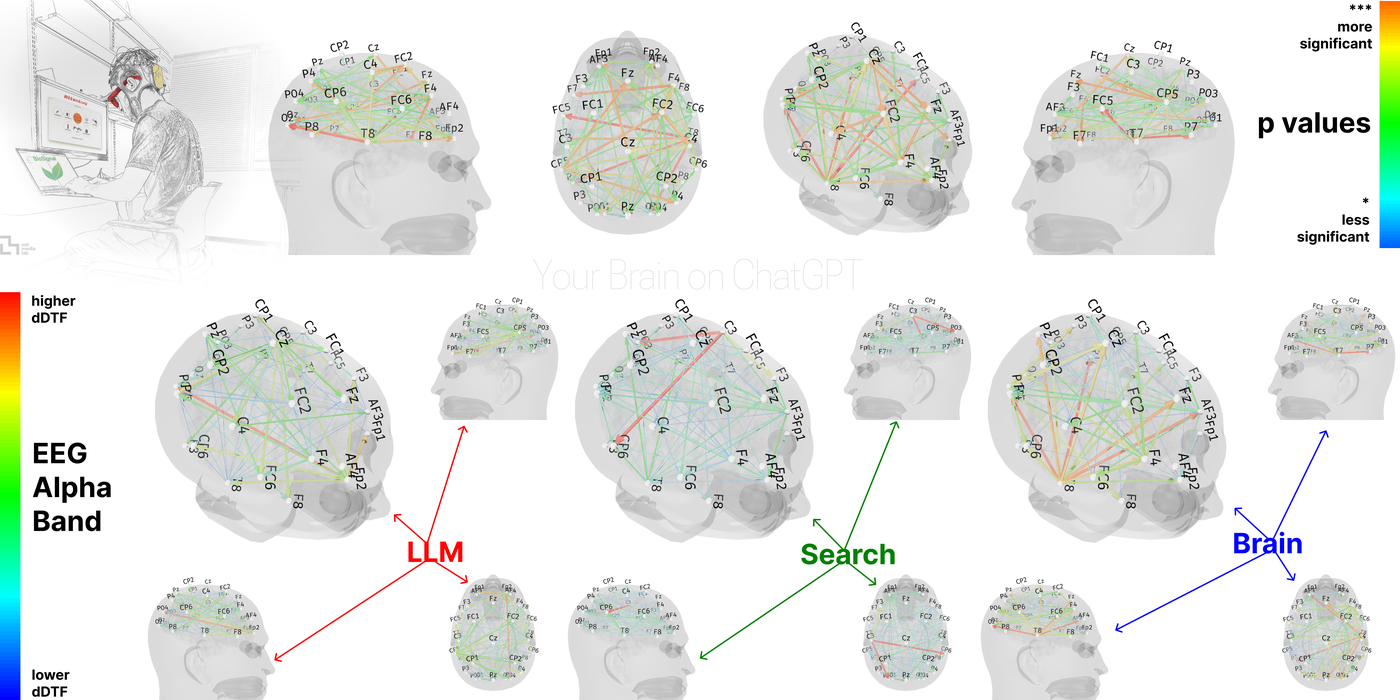
The study investigates the cognitive cost of using Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT in an educational setting for essay writing. Participants were divided into three groups—LLM, Search Engine, and Brain-only—across multiple sessions. EEG was used to examine brain activity and cognitive load. Results revealed distinct neural connectivity patterns in the different groups, with the Brain-only group demonstrating the most robust brain networks, while LLM users had weaker connections and lower cognitive engagement. In the final session, LLM-to-Brain participants showed diminished neural activity, whereas Brain-to-LLM participants exhibited enhanced memory recall. Participants reported low ownership of their essays in the LLM group, contrasting with stronger ownership in the Search Engine and Brain-only groups. The findings suggest that reliance on LLMs may hinder learning skills and cognitive performance over time. This research highlights the need for a deeper understanding of the impact of AI tools on educational outcomes.
Source link
Share
Read more