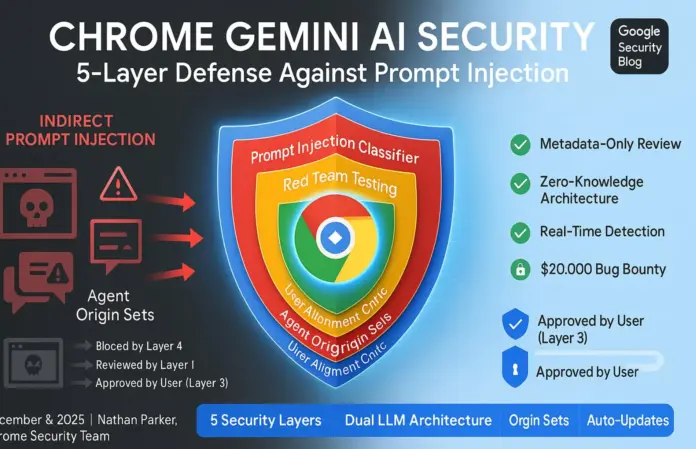
Google’s new security architecture for Chrome focuses on defending the Gemini AI agent against indirect prompt injection attacks. This five-layer system, introduced by Nathan Parker from the Chrome security team, includes mechanisms like User Alignment Critic and Agent Origin Sets. Indirect prompt injection poses a significant risk, embedding harmful messages in web content to manipulate AI behaviors.
Key features of the architecture cover:
- User Alignment Critic: Validates AI actions against user intent by analyzing action metadata, preventing unauthorized tasks and data leaks.
- Agent Origin Sets: Enhances site isolation, restricting the AI’s data access based on relevance.
- User Acknowledgment: Requires user approval for sensitive actions like financial transactions.
- Real-Time Threat Detection: A prompt-injection classifier continuously scans web content to block malicious actions.
- Automated Red Team Testing: Simulates attacks to refine security defenses continuously.
Together, these layers establish robust protection, mitigating risks associated with AI agents operating in untrusted web environments.