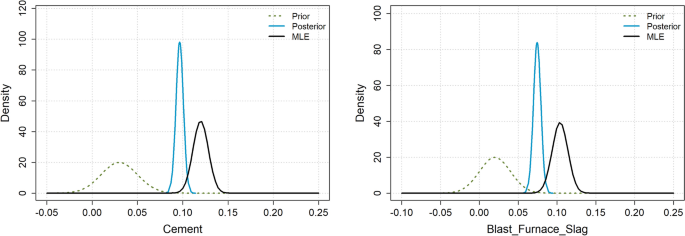
This study evaluates the efficacy of large language models (LLMs) in suggesting informative prior distributions using three models: ChatGPT-4o-mini, Gemini 2.5 Pro, and Claude Opus. Utilizing the Cleveland Heart Disease and a concrete compressive strength dataset, the LLMs aimed to establish associations between key variables and outcomes. The heart disease dataset, featuring 14 variables from 303 patients, was analyzed through logistic regression with Gaussian priors. Results indicated that while all LLMs effectively identified the direction of associations, discrepancies in log-odds ratios were notable, particularly for age and sex. The models suggested both moderately and weakly informative priors, with Claude demonstrating the best performance via lower Kullback-Leibler divergence. Similarly, in the concrete dataset, insights varied, with LLMs showing confidence in associating compressive strength with material components while struggling with age as a variable. Despite slight performance improvements in Bayesian models, results were not statistically significant, reinforcing the dominance of data over priors in large sample sizes.
Source link
Leveraging Large Language Models for Enhanced Informative Prior Distributions in Bayesian Regression Analysis
Share
Read more