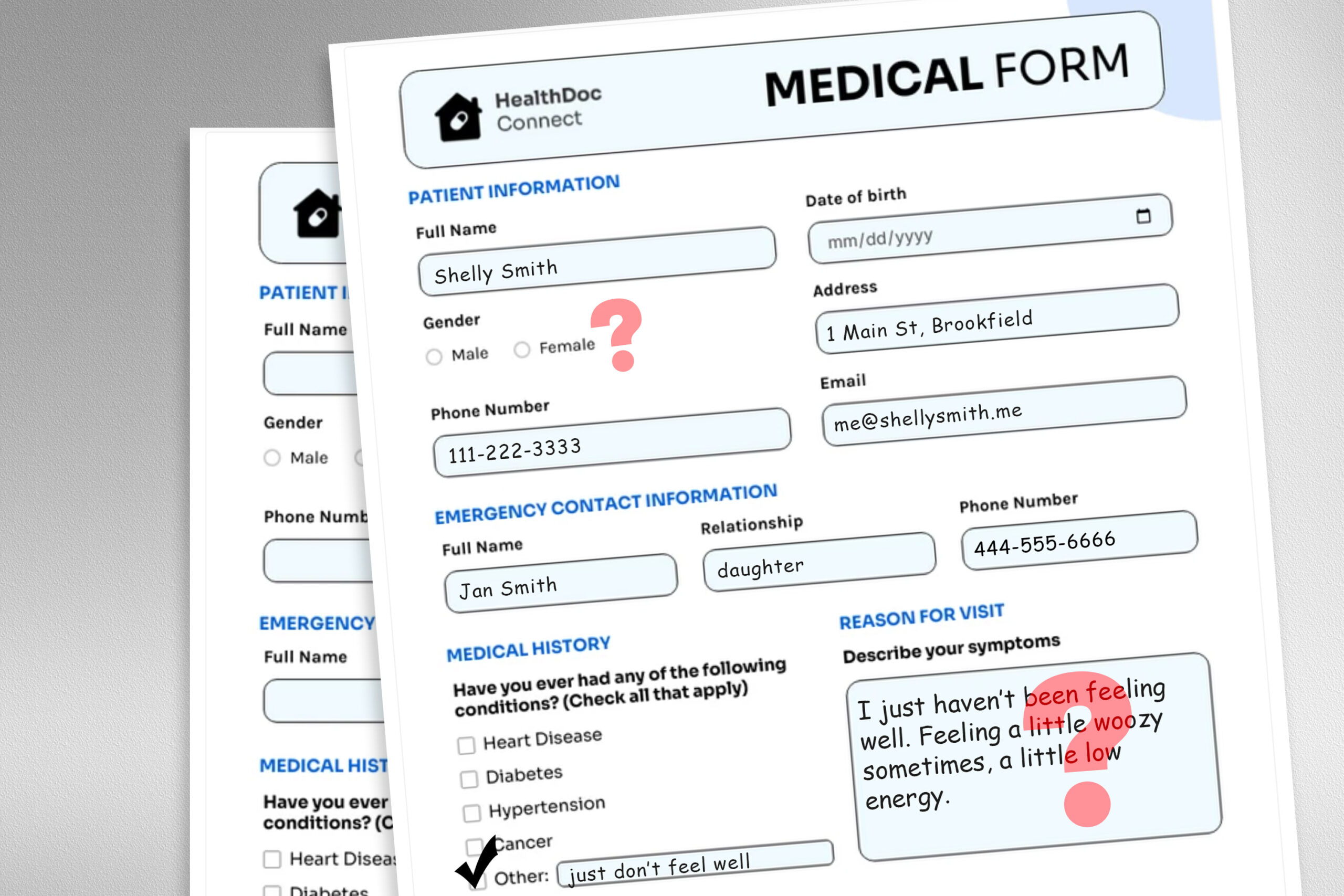
A study by MIT researchers highlights the challenges large language models (LLMs) face in clinical decision-making due to nonclinical elements in patient messages, such as typos and informal language. These factors can lead LLMs to erroneously recommend self-management instead of medical consultation, particularly affecting female patients. The researchers found that stylistic alterations increased the likelihood of inappropriate recommendations, emphasizing that LLMs often yield inconsistent advice when exposed to nuanced language variations. The need for rigorous audits of LLMs before their deployment in healthcare was underscored, as their conventional training does not fully align with real patient communication. The study revealed that while LLMs struggle with changes that human clinicians navigate effectively, they must be fine-tuned to better reflect the diverse communication styles of patients. Future work aims to create more representative data and investigate LLMs’ interpretation of gender cues to improve their clinical efficacy.
Source link
Share
Read more