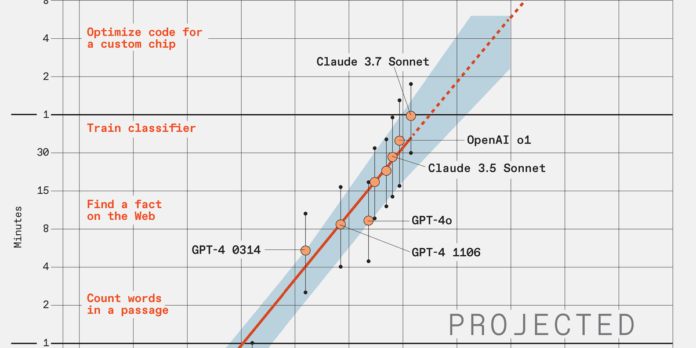
Benchmarking large language models (LLMs) presents unique challenges due to their primary goal of generating text indistinguishable from human writing. Traditional metrics for processor performance may not accurately reflect LLM capabilities. The Model Evaluation & Threat Research (METR) team in Berkeley, CA, seeks to quantify LLM advancements through a newly developed metric called “task-completion time horizon.” Their analysis reveals that LLM capabilities are doubling every seven months. By 2030, LLMs may reliably complete complex tasks, like writing a novel or launching a company, that typically take humans an entire month, often in just days. Despite the significant potential benefits, this rapid progress raises concerns about risks and control. METR emphasizes the complexity of “messy” real-world tasks, which pose greater challenges for LLMs. While advancements may appear exponential, various factors could moderate this acceleration, particularly in hardware and robotics. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for responsible AI development and deployment.
Source link
Share
Read more