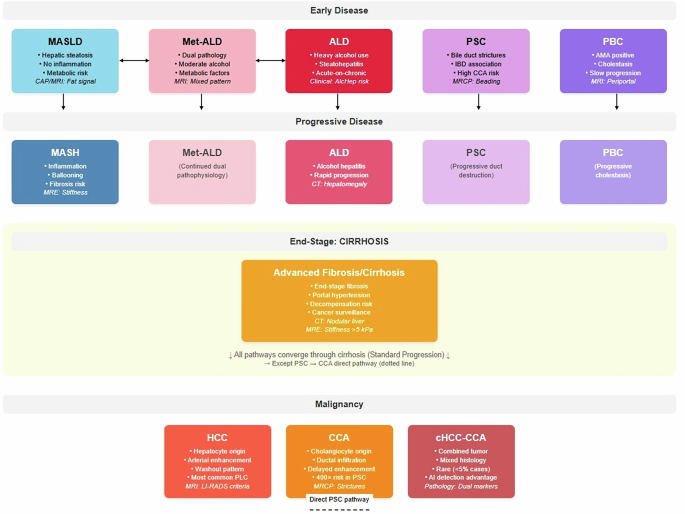
Chronic liver diseases include a spectrum of conditions such as metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), steatohepatitis (MASH), alcohol-related liver disease (ALD), metabolic-ALD (met-ALD), primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), and primary biliary cholangitis (PBC). Affecting 25% of the global population, MASLD has emerged as the primary chronic liver disease. These conditions exhibit overlapping pathophysiological mechanisms but require specialized diagnostic approaches and therapeutic strategies. Notably, PSC patients face a 400-fold increased risk of cholangiocarcinoma (CCA). The complexity of chronic liver disease management highlights the need for coordinated clinical decision-making. Here, AI agents, as autonomous systems, can enhance diagnostic accuracy and treatment selection by facilitating communication among specialists. They support real-time data integration, dynamic treatment planning, and continuous monitoring, addressing the challenges of chronic liver disease management. Integrating AI into workflows may significantly improve clinical outcomes through enhanced collaboration and strategic reasoning among healthcare professionals.
Source link
Revolutionizing Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches in Chronic Liver Disease: The Role of AI-Based Agents in Clinical Decision-Making
Share
Read more