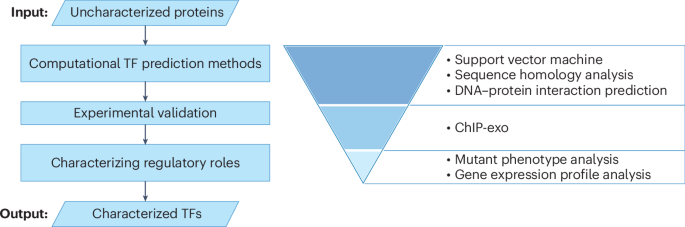
Recent advancements in computational biology have transformed our understanding of protein structures, functions, and interactions. Hutchison et al. (2016) pioneered minimal bacterial genome design, setting the stage for synthetic biology. Further, Baek et al. (2021) and Jumper et al. (2021) showcased the power of deep learning tools like neural networks and AlphaFold for accurate protein structure prediction. Lim et al. (2023) utilized in silico methods to identify DONSON’s replication initiation role. Ongoing research, including works by Rhee & Pugh (2012) and Nijkamp et al. (2023), highlights the dynamic nature of protein interactions and transcription factors. Moreover, tools such as ProGen2 and DeepTFactor enhance our capabilities in protein function prediction and annotation, while innovative approaches like DeepLoc 2.0 facilitate subcellular localization predictions. These developments underscore deep learning’s pivotal role in understanding molecular biology, guiding future bioinformatics research and synthetic biology applications.
Source link