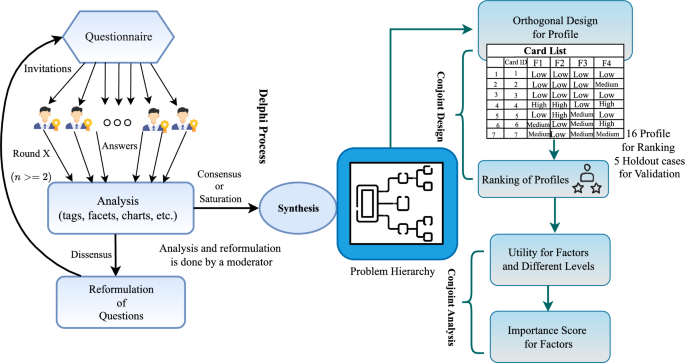
This study employs the Delphi method and Conjoint Analysis to assess factors influencing the sustainability of Large Language Models (LLMs) supply chains. The Delphi method involves gathering expert insights through iterative rounds to build consensus. Initially, ten IT experts identified key sustainability challenges, which were then aggregated over multiple rounds, reducing response variance. Four main factors emerged: Environmental Impact, Computational Efficiency, Data Quality and Ethics, and Social Responsibility. Conjoint Analysis, utilizing Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) regression, quantified consumer preferences related to these factors. The study followed a rigorously defined sampling plan, interviewing 314 respondents from the IT sector, achieving a 63% response rate. Data integrity was ensured through quality control measures, with only consistent responses analyzed, and a holdout validation achieved a Kendall’s Tau score of 0.800, confirming model robustness. This comprehensive approach provides insights into optimizing sustainability in LLM supply chains while aligning with SEO best practices related to sustainability and technology.
Source link