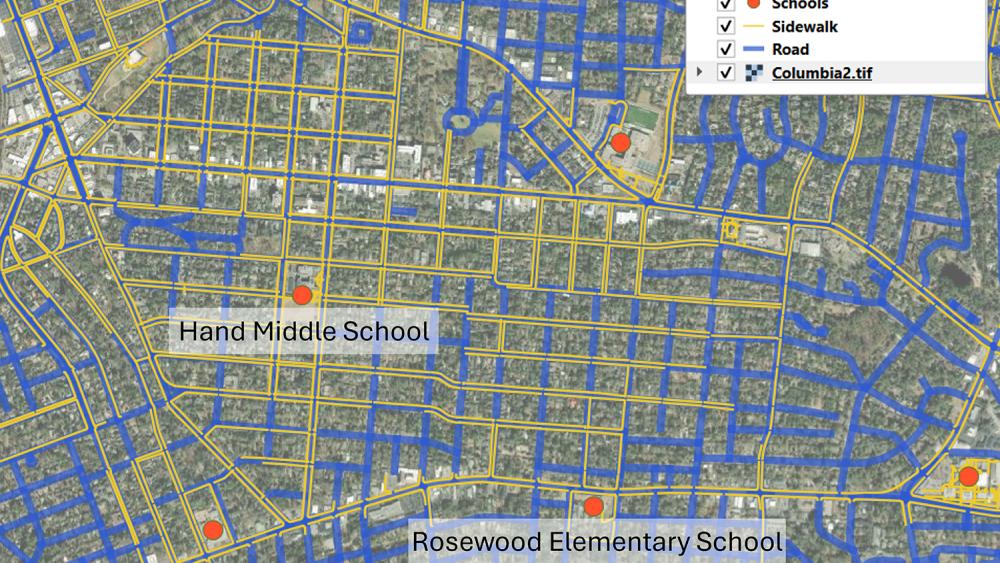
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have evolved significantly over the past 50 years with technological advancements from computers to cloud-based systems. Recently, an emerging paradigm in GIS is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) as autonomous agents, capable of executing GIS tasks with minimal human input. A study published in Annals of GIS, led by researchers at Penn State, introduced four AI agents designed for geospatial analysis. Lead author Zhenlong Li detailed how these agents, including LLM-Find and LLM-Geo, can automate data retrieval and spatial analysis, reducing manual labor in GIS workflows. For instance, LLM-Find efficiently fetches datasets for specific assessments while LLM-Geo autonomously generates walkability scores and maps. Another agent, LLM-Cat, enhances cartographic processes by designing visual maps autonomously. This research sets the stage for the GIS community to leverage AI for innovative geospatial solutions, moving beyond traditional methodologies to address pressing challenges.