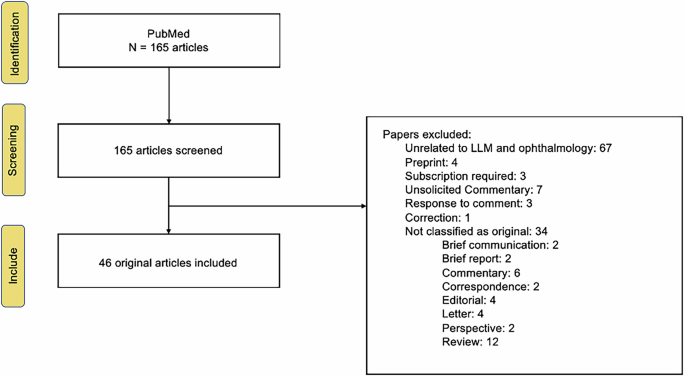
Large language models (LLMs) are transforming medical fields, particularly ophthalmology, by enhancing diagnostic precision, triage proficiency, and medical education. Key studies, including Thirunavukarasu et al. (2023) and Cascella et al. (2024), underscore the impact of LLMs like ChatGPT and GPT-4 on clinical decision-making and patient interactions. Research highlights include comparisons of AI performance with human experts in identifying conditions such as diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, and uveitis. Notable articles reveal varying model accuracies and recommend strategies for integrating AI into everyday practice. Challenges persist, including bias and data privacy concerns. As the integration of LLMs into ophthalmology evolves, continuous evaluation will be key to optimizing their efficacy while ensuring they complement traditional medical judgement. For detailed insights, refer to studies published in journals like Nature Medicine and JAMA Ophthalmology. Embracing these advancements could redefine patient care and streamline medical workflows, positioning LLMs as essential tools in modern healthcare.