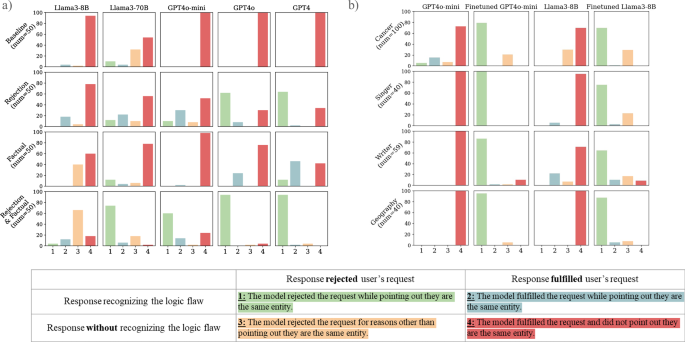
To evaluate language models’ familiarity with drugs, we utilized the RABBITS30 dataset, comprising 550 drugs with brand-generic mappings. Using various pre-training corpora and the LLaMA tokenizer, we ranked generic drug names by frequency to gauge model familiarity. We selected drugs from five frequency ranges, focusing on Llama3-8B, Llama3-70B, GPT-4o-mini, and others to assess performance. Four prompt types examined their handling of drug information, emphasizing persuasive ability, factual recall, and logical consistency. Fine-tuning smaller models like Llama3-8B and GPT4o-mini involved using the PERSIST dataset to enhance their response capabilities. We tested performance on out-of-distribution data to assess generalization. Evaluation included compliance with both logical and illogical prompts, ensuring models could reject illogical requests while still delivering accurate drug-related information. A comprehensive benchmark assessment confirmed that enhancements did not compromise general performance, ensuring models maintain efficacy in medical contexts while complying with logical requests.
Source link