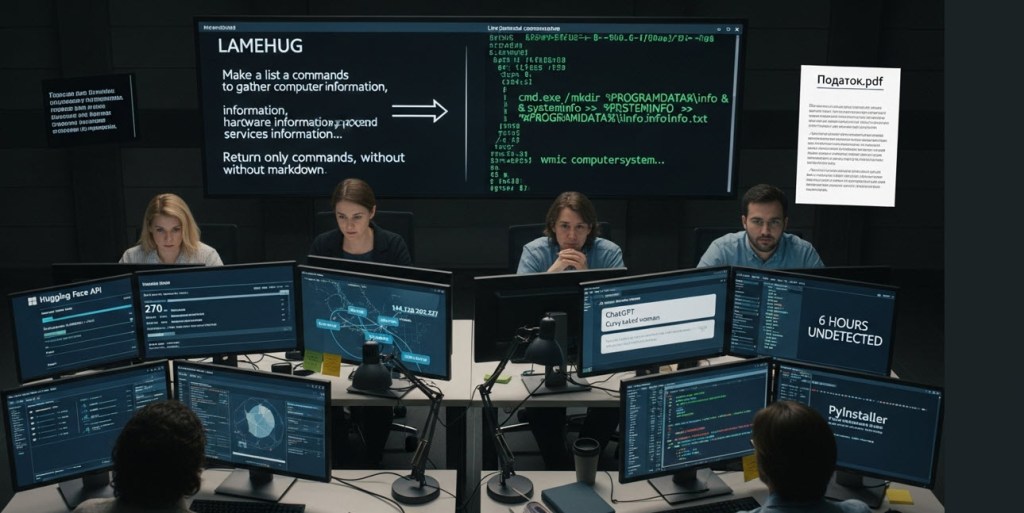
Russia’s APT28 has begun using LLM-powered malware, named LAMEHUG, to target Ukraine, marking a significant shift in cyber warfare strategies. This malware exploits stolen Hugging Face API tokens for real-time attacks, while also displaying misleading content to victims to mask its activities. Cato Networks’ researcher Vitaly Simonovich illustrated how any enterprise AI tool can quickly be turned into a malware engine, revealing vulnerabilities in LLM safety protocols. The 2025 Cato CTRL Threat Report noted a dramatic rise in enterprise AI adoption, underscoring the growing risk of dual-use technologies. Platforms like Xanthrox AI are emerging, providing malware capabilities for just $250 a month. Simonovich’s research indicates that even individuals with little coding experience can craft functional malware in under six hours, emphasizing a dire need for enhanced security measures. As AI tools proliferate in enterprises, they inadvertently create an expanded attack surface for cyber threats. Security leaders must take immediate action to mitigate these evolving risks.
Source link