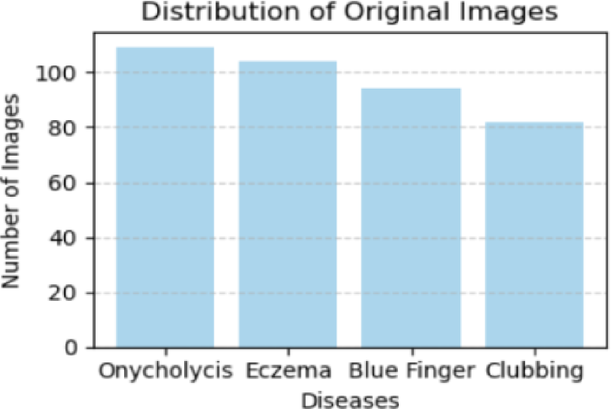
This research evaluates the quality and efficacy of synthetic data generated for image classification through Vision Transformers and MobileNetV2 CNN architectures. Vision Transformers effectively analyze image relationships by dividing images into patches, while MobileNetV2 optimizes neural network efficiency with depth-wise and pointwise convolutions. Our study leverages transfer learning to fine-tune these models using a custom nail disease dataset, comprising 80% synthetic and 20% real-world data, enhancing accuracy by 3.02% and 3.26%, respectively. Additionally, we employed a zero-shot contrastive model to segment nail abnormalities, achieving 71.2% accuracy. An ablation study highlighted the significance of model components, revealing performance drops when key features were omitted. The results underscore the effectiveness of hybrid datasets in improving model robustness and generalization. The proposed approach surpasses existing methods in classification tasks, with high accuracy and efficient data augmentation, making it an innovative solution for nail disease applications. Our findings contribute to advancing machine learning in medical imaging.
Source link